Introduction
Rudolf
Diesel a German engineer was the person who has introduced the Diesel engine in
1890s.
at that time they used coal as fuel and this invention had
done great revolution in mechanical scheme.
After 7 years he invented a compression ignition engine which
is run in kerosene.
These
engines are very effective and low cost in inner operation. Consume less fuel.
So these
types of engines were very popular
in that time. At that time and now also they are being use in big and
heavyequipmentshipping and railways. In these
days most heavy duty busses, trucks, trains and autom
obiles also get poweusing these
types of engines.
Most
commonly Diesel engines produce energy and heat by air compression ignition in
fuel insid
the cylinder. (Internal combustion
engine).When the fuel (Diesel) coming in side of the cylinder there
exists hot air and that air have enough heat
to burn the fuel. Therefore it does not need spark plugs. It is
a very much advantage.Diesel engines burn petroleum products like kerosene,
jet fuels etc.
Inside
a diesel engine also there are cylinders and pistons. When the piston moves up
and down
inside the cylinder the connecting rod which is connected to the
piston is transmitting power to crank
shaft to rotate it.This is the
basic operation inside the engine.
Diesel
engines are combust the fuel air mixture by compression. Therefore it should
apply higher
load to the pistons and cylinders.
So the inner and outer components should be having great strength to
withstand this much of higher
forces and pressure. Due to these components are very strong the cost to
make them also is high. Therefore the cost of the engine is also very high.
Perkins engine is a 4 cylinder, 4
stroke diesel engine, that means the internal combustion happens in four
strokes in side the cylinder
Here
is the brief introduction about four strokes in Perkins diesel engine.
· Intake stroke: - In this stroke cylinder sucks
air by opening the inlet valve. In this stroke piston is
in Bottom Dead Center.
·
Compression stroke: – In here intake valve
closed and piston moves up to the cylinder. Within this
strok air will compress highly and reached high temperature. At the
finishing of
this stroke fuel will be injected.
· Combustion stroke: – Pressure and temperature
will be increased due to the combustion happens.
Therefore piston moves down.
·
Exhaust stroke: – At the beginning of this
stroke piston in its bottom position. During this stroke piston coming up and outlet valve will open
simultaneously. So the exhaust
gasses can
move from the cylinder.
Perkins Diesel Engine
Inside the Four cylinders four
stroke Engine With all four strokes..
Theory
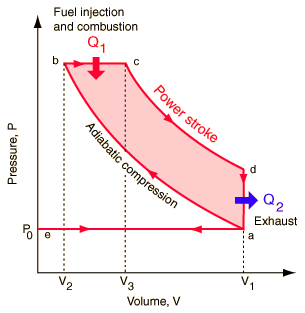
Basic Diesel Cycle
·
Process a-b : Isentropic compression
·
Process b-c:
Reversible constant pressure heating
·
Process c-d : Isentropic expansion
·
Process d-a : Reversible constant volume cooling
By this experiment we are trying
to get some knowledge about Perkins diesel engine with its design and
operations and the performance in several circumstances such as fuel
consumption ,efficiency etc.
Useful Notations;
V Volume
T Temperature
Q Heat
γ Cp
/ Cv
Cp Specific
heat capacity under constant pressure
Cv Specific
heat capacity under constant volume
α Cut-off ratio = V3 / V2
r
Compression ratio = V1 / V2
U Internal
Energy
η=
Net work / Work in
According to
the 1st law of thermodynamics,
∆U = ∆Q - ∆W
∆U=0, therefore
∆Q = ∆W
Net work = net
heat = Q(bc) + Q(da)
Work in = heat
in =
Q(bc)
η=Q(bc)
+ Q(da) / Q (bc)
η=1 + [Q(da) / Q (bc)]
Q(bc) = Cp (Tc - Tb)
Q(da) = Cv (Ta - Td)
Standard notation
BP = Brake power
FP = Friction power
IP = Internal power
K (constant) = 4500
W = load (lbs)
N = Speed (rpm)
SFC = Specific fuel consumption
BPMF = Brake power mean efficiency
BMEP = Brake mean effective pressure
h = Manometer water head (inch
of water)
T = temperature at the orifice
(K)
H = Atmospheric pressure (inch
of Hg)
d = Orifice diameter
D = Cylinder bore
L = Stroke
BP= W.N/K (kW)
IP = BP + FP
BMEP = BP / (Π / 4. D^2. L. (N /
2) (4 / 60) )
Volume inhaled = (4.193 / 35.22)
D^2. ( h.T / H) ^ 0.5 (m^3 / min)
Swept volume = 4. (Π / 4 D^2 L). N
/2 (m^3 / min)
Performance parameters
SFC = (Fuel consumption / BP).
3600 (kg / kWh)
Mechanical efficiency = BP / IP
Brake thermal efficiency = overall
efficiency = BP / Rate of heat input by the fuel
Volumetric efficiency = volume
inhaled / Swept volume
Indicated thermal efficiency = IP
/ Rate of heat input
Calculation of frictional power
This
can be observed from the graph of fuel consumption vs. brake power. We have to
get thefuel consumption in zero power, because when frictional power will be
available only when the brake power is zero in the engine. So the frictional
power will equal to internal power.
Internal power
= Frictional power + Brake power
Brake
power = 0
Therefore,
Internal
power = Frictional power
Frictional power = (Fuel
consumption where the brake power is zero) * Calorific value
Heat balance
Rate of heat =
internal + Rate of heat rejection + Rate
of heat rejection
input
by the fuel power by the water by the exhaust gas
Procedure
1.
Open the inlet water supply valve fully and the outlet
valve slightly of the dynamometer.
a.
i.e. Dynamometer: Instruments measuring energy
expended.
2.
Make sure all the valves in the piping between the
source of the water supply and the dynamometer inlet are fully open.
3.
The engine may now be started.
4.
Loads may be regulated by opening the sluice gates by
means of the hand-wheel and simultaneously operating the engine throttle, until
the desired load and speed are obtained.
5.
Adjust the outlet valve to pass sufficient water to
keep the temperature at a reasonable figure.
6.
A hand wheel is provided on top of the balance frame to
adjust the height of the balance arm. Make sure that this wheel is always set
to the horizontal position when taking B.HP readings.
Equipment
·
Perkins diesel engine.
·
4 cylinder 4 stroke engine
·
coolant
:- water cooled
·
Engine is coupled with a Henan-Froude water
cooled dynamometer, So the torque, speed
in rpm,
·
can be
measured.
·
Measuring air mass flow rate: - an orifice plate
fitted to an air reservoir this is attached to the inlet manifold of
the engine.
·
Measuring pressure across the orifice: - Using
an inclined water manometer.
Engine parameters
·
Orifice diameter = 2.05 inches
·
Length of the stroke = 3.05 inches
·
Cylinder bore = 3 inches
·
Speed of rotation = 1500 rpm
Fuel parameters
·
Specific heat capacity of the fuel = 1.08kg / kJ.K
·
Density of the fuel = 880 kg /m^3
·
Calorific value of fuel = 44290 kJ/kg
Discussion
Perkins engine is a diesel engine which is
working according to the diesel cycle. Because of these
advantages of the diesel cycle we
can convert this Perkins engine to be very effective engine which
having more efficiency, high fuel
consumption, smoothness etc. we can enhance high performances
using Perkins engine than gasoline or other
fuel engines by internal combustion.
There
were many differences between traditional gasoline engine and Perkins engine.
We can categorize this are basic two
categories.
·
Ignition method
Gasoline
:- Spark Ignition
Diesel
:- Compression Ignition
·
Fuel Injection
Gasoline
:- port fuel injection.
Diesel
:- Direct fuel injection.
Advantages and
Disadvantages of Perkins Diesel Engine.
Advantages:-
·
This engine has high expansion ratio and reached
high temperature in combustion. Due to these reasons Diesel engine has mare efficiency
and greater fuel efficiency than other engines. Gasoline engines basically
having 20-25% efficiency while Diesel engines have efficiency more than 30%.
·
They are no high powered electrical ignition
system to burn fuel. So it is not more harmful to environment because there are
no use of carbon coils, wires, unwanted metals and also it eliminates a source
of radio frequency emissions which are connect with communication and
navigation.
·
For a given load to the engine, Diesel engine
remains its efficiency constant while at that load gasoline engine reduces its
efficiency to put more output powers.
·
Life time of the Diesel engine is approximately
twice a gasoline engine Due to the diesel engine are made by high strength
metal parts than traditional gasoline engines.
·
Can deliver the generated power continuously
than the gasoline engine.
·
High compression ratio. Volume of the cylinder
when the piston at BDC to the volume of the cylinder when the piston at the
TDC.
- When higher Compression ratios,
·
The temperature of air is higher at the end of
the compression stroke,
·
Having higher thermal efficiency,
·
Greater fuel economics,
·
Generate high temperatures required for auto
ignition.
·
Also Diesel engines actually the fuel diesel is
more safer than other fuel like petrol. Though diesel get fired in normal air with
the support of some fire pulse, it does not explore in severe manner like
petrol. It would be great advantage for the industry.
·
And the law vapor pressure of diesel gives more
advantage for marine applications. So the fuel air mixtures which is accumulation of
explosive is extremely hazard and for while diesel engines are immune to vapor
locking.
·
Compression Ratio of Diesel Engine to Gasoline
Engine
- Spark ignition compression ratio 8:1 to 12:1
- Compression ignition ratio 14:1 to 25:1
·
Compression ratio of Diesel engine
- The Compression ratio indicates that in how much of strength the cylinder can compromise it’s contain to outside. As the figure indicates the engine which is used otto cycle is having a smaller compression ratio than the diesel engine. So the engine can work with high efficiency and it also very important for industrial and other applications.
Disadvantages:-
·
Main disadvantage is that the Diesel engine
emits Carbon Monoxide with its exhaust gas. This affects the surrounding and
our environment. But this is very small by comparing the gasoline engine. Because, gasoline engine emits
unburned fuel parts and several other chemical components which are more
harmful to surrounding as well as human beans.
·
Another disadvantage is that in this diesel
engine fuel injected before power stroke. If there is nit sufficient air to get
that fuel so fuel will not burned 100% correctly. So that incomplete combustion
make exhaust gas black in color and very thick and this unburned fuel will
reaches outer environment and it is not very safer.
·
Other thing is those engines are very expensive
than other engine types. Because it cost highly in manufacturing and
maintenance. Diesel engines are very echo friendly than other engines and they
are having high technology to reduce the various components in exhaust system.
So this increases its price than other models.
·
When the engine working it emits high noise.
This is called as Diesel knock and this noise caused because the diesel
combustion process and sudden ignitions.
·
Diesel engines have long stroke lengths to
achieve higher compression ratios. So the connecting rods and crankshaft are
very heavy and the required power to transmit power is very high.